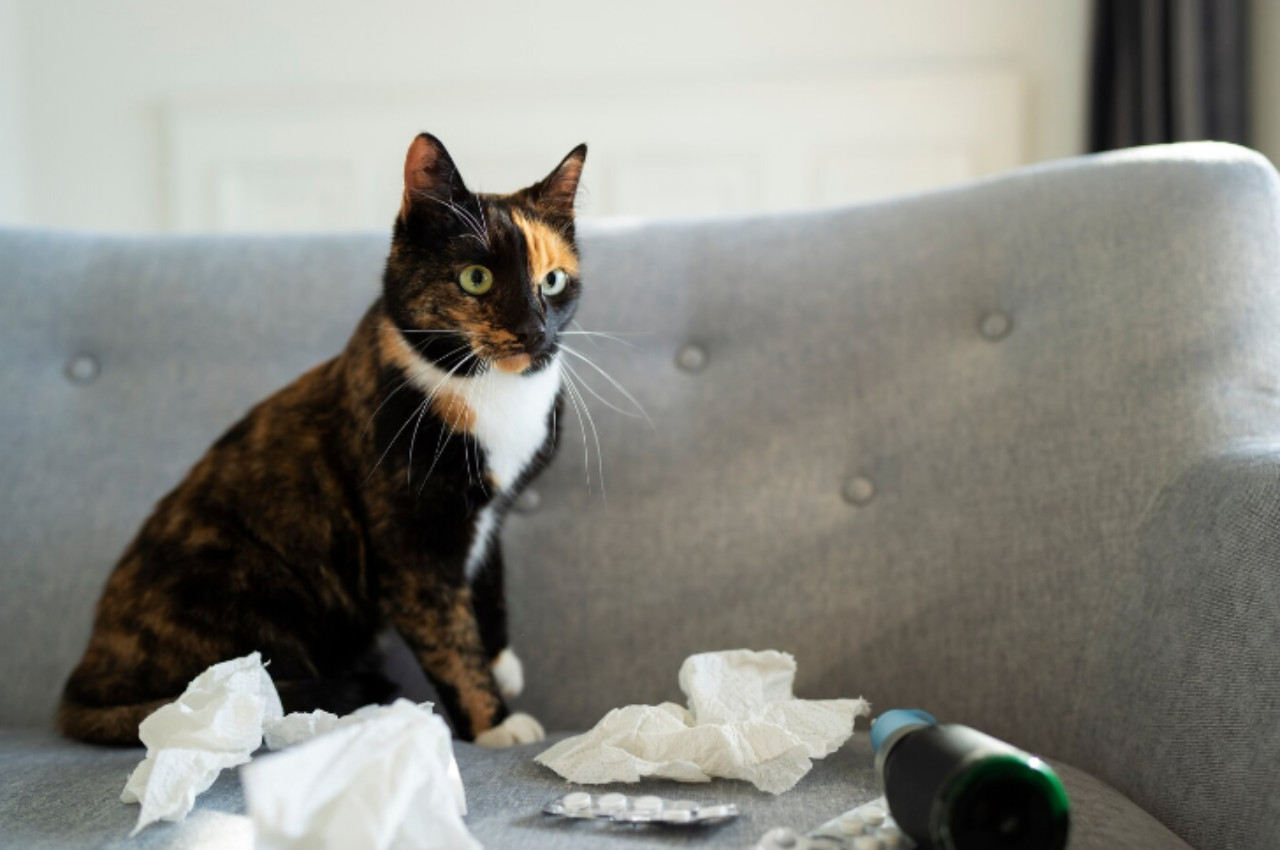
To tell if a cat is traumatized, observe for hiding, aggression, or changes in eating habits. Traumatized cats may also show increased vocalization or litter box issues.
It’s essential to monitor their behavior closely to provide appropriate care and support. Understanding the signs of cat trauma can help you address the issue promptly and ensure your feline friend’s well-being. By recognizing these indicators early on, you can take steps to help your cat feel safe and secure in their environment.
Let’s explore some common signs of cat trauma and how you can assist your pet in overcoming these challenges.
Introduction To Feline Trauma
Identifying feline trauma involves observing changes in behavior like excessive hiding, aggression, or loss of appetite. Other signs include excessive grooming, dilated pupils, or avoiding human contact. Understanding these cues can help in providing the necessary support and care for a traumatized cat.
Cats are known for their agility, independence, and resilience. However, just like humans, cats can also suffer from psychological trauma. Feline trauma can occur due to various reasons, such as accidents, abuse, illness, or even changes in their environment. It is essential to understand the signs of trauma in cats to provide them with the necessary support and care they need to recover. In this blog post, we will discuss the common causes of trauma in cats and why recognizing trauma is crucial for their well-being.
Common Causes Of Trauma In Cats
There are several common causes of trauma in cats, including:
| Causes | Description |
| Accidents | Physical injuries from falls, car accidents, or other mishaps can cause trauma in cats. |
| Abuse | Cats that have been physically or emotionally abused may experience trauma that affects their behavior and trust towards humans. |
| Illness | Cats that have suffered from serious illnesses or injuries may experience trauma due to the pain and discomfort they have endured. |
| Changes in Environment | Cats are creatures of habit, and any significant changes in their environment, such as moving to a new home or the addition of a new pet, can cause trauma. |
Why Recognizing Trauma Is Crucial
Recognizing trauma in cats is crucial because it can affect their overall well-being, behavior, and quality of life. Traumatized cats may exhibit signs of fear, aggression, or withdrawal, which can lead to problems in their relationships with their owners and other pets.
Moreover, if left untreated, trauma can lead to long-term physical and psychological problems that may require extensive treatment. Therefore, it is essential to monitor your cat’s behavior and seek professional help if you suspect they may be suffering from trauma. In conclusion, trauma can happen to any cat, regardless of their age, breed, or temperament. By understanding the common causes of trauma and recognizing the signs, you can provide your cat with the necessary support and care they need to recover and live a happy life.
Physical Symptoms Of Trauma In Cats
Recognizing the physical symptoms of trauma in cats is crucial for providing the necessary care and support. Cats, like humans, can experience trauma that manifests in various physical signs. Being attentive to these signs can help in identifying and addressing any potential issues. Here are some common physical symptoms of trauma in cats:
Changes In Appetite Or Weight
Noticeable changes in a cat’s appetite or weight can indicate trauma. This can manifest as a sudden increase or decrease in food consumption, or significant fluctuations in weight. Some cats may exhibit a refusal to eat altogether, while others may engage in excessive overeating as a response to stress.
Unusual Sleeping Patterns
Abrupt changes in a cat’s sleeping patterns, such as excessive sleeping or insomnia-like behavior, can be indicative of trauma. Cats may display restlessness or difficulty settling down for sleep, often due to heightened anxiety or stress.
Visible Injuries And Their Implications
Visible physical injuries, such as scratches, bruises, or limping, can be direct indicators of trauma in cats. These injuries may be the result of conflict with other animals, accidents, or self-harm as a response to emotional distress. It’s important to address these injuries promptly and seek veterinary attention if necessary.
Behavioral Signs Of Traumatized Cats
Cats show behavioral signs of trauma through excessive hiding, aggression, or withdrawal. They may also display changes in eating or grooming habits, and exhibit fear or anxiety. Understanding these signs can help in providing the necessary support and care for a traumatized cat.
Increased Aggression Or Fear
One of the key behavioral signs of a traumatized cat is an increase in aggression or fear. Trauma can cause a cat to become defensive and lash out, even towards their owners. They may hiss, growl, or swat at people or other animals, displaying an unusual level of aggression. Additionally, a traumatized cat may exhibit heightened fear and become easily startled or frightened by their surroundings.
Hiding And Avoidance Behaviors
Hiding and avoidance behaviors are common in traumatized cats. They may retreat to secluded areas of the house, such as under the bed or in closets, seeking a safe space where they feel protected. Traumatized cats may also avoid social interactions and become more withdrawn. They may refuse to engage with their owners or other pets, preferring to isolate themselves instead.
Changes In Grooming Habits
Another behavioral sign of a traumatized cat is changes in their grooming habits. Cats are known for their meticulous grooming routines, but trauma can disrupt this behavior. A traumatized cat may over-groom, causing bald patches or skin irritations. On the other hand, they may also neglect grooming altogether, leading to a disheveled and unkempt appearance.
Emotional Indicators Of Feline Trauma
Cats, like humans, can experience emotional trauma due to various factors such as abuse, neglect, or major life changes. Recognizing the emotional indicators of feline trauma is crucial for providing the necessary support and care for the well-being of your cat.
Signs Of Depression In Cats
Depression in cats may manifest as decreased activity, changes in appetite, or excessive sleeping. Withdrawal from social interaction and lack of interest in play are also common signs of feline depression.
Anxiety And Its Manifestations
Anxiety in cats can be exhibited through excessive grooming, hiding, or destructive behavior. Agitation, restlessness, and hypervigilance are also indicative of feline anxiety.
Attachment Issues Or Clinginess
Cats experiencing trauma may display clinginess, seeking constant reassurance, or displaying signs of separation anxiety. Conversely, they may also exhibit detachment and aversion to physical contact.
The Impact Of Trauma On A Cat’s Health
Understanding the impact of trauma on a cat’s health is crucial for pet owners to provide the necessary care and support. Cats, like humans, can experience trauma from various sources, including abuse, accidents, or sudden changes in their environment. Recognizing the signs of trauma is essential to help the cat heal and prevent long-term health complications.
Long-term Effects Of Trauma
Trauma can have long-term effects on a cat’s physical and emotional well-being. Cats may exhibit signs of anxiety, aggression, or withdrawal, which can impact their overall quality of life. Additionally, trauma may lead to chronic health issues such as digestive problems, respiratory issues, or skin conditions. These long-term effects highlight the importance of addressing trauma in cats and providing the necessary support for their recovery.
The Link Between Trauma And Illness
Trauma can be linked to various illnesses in cats, affecting their immune system and overall health. Cats that have experienced trauma may be more susceptible to infections, allergies, and autoimmune disorders. Furthermore, the stress and anxiety resulting from trauma can weaken the cat’s immune response, making them more prone to illnesses. Understanding this link is essential for pet owners to prioritize their cat’s mental and physical well-being.
How To Approach A Traumatized Cat
Recognizing a traumatized cat involves observing changes in behavior, such as excessive hiding, aggression, or withdrawal. If your cat displays these signs, approach them calmly and avoid sudden movements. Create a safe, quiet space and give them time to adjust, offering gentle reassurance and patience.
Creating A Safe Environment
To approach a traumatized cat, creating a safe environment is crucial. Place hiding spots and vertical spaces for comfort.
The Importance Of Patience And Space
Patience and space are key. Allow the cat to come to you at their own pace.
When To Seek Professional Help
If a traumatized cat shows severe signs of distress, seek professional help immediately. A veterinarian or animal behaviorist can provide the necessary support.
Treatment Options For Traumatized Cats
Behavioral Therapy And Its Benefits
Behavioral therapy helps traumatized cats by addressing negative behaviors and promoting positive ones.
Medications: Pros And Cons
Medications can help calm anxious cats but may have side effects and require careful monitoring.
Alternative Therapies And Holistic Approaches
Alternative therapies like acupuncture and holistic approaches such as aromatherapy can aid in reducing cat stress.
Preventing Future Trauma
Cats can show signs of trauma through changes in behavior, such as excessive hiding, aggression, or avoidance. Other indicators may include loss of appetite, increased vocalization, or unusual litter box habits. It is important to observe these behaviors and seek professional help to prevent further trauma and provide necessary care for your cat.

Creating A Stable Environment
To prevent future trauma, creating a stable environment is key.
- Provide consistent routines and safe spaces.
- Use positive reinforcement for good behavior.
Training And Socialization Tips
Proper training and socialization can help prevent trauma in cats.
- Introduce new experiences gradually.
- Encourage positive interactions with people and animals.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups And Their Importance
Regular vet check-ups are essential for a cat’s well-being.
| Benefits | Importance |
| Early detection of health issues | Prevents future complications |
| Vaccinations and preventive care | Boosts immunity |
Conclusion
Recognizing signs of trauma in cats is crucial for their well-being and happiness. By observing their behavior, body language, and physical symptoms, we can identify if a cat is traumatized and take the necessary steps to help them heal. Providing a safe and nurturing environment, seeking professional help if needed, and offering patience and understanding are essential in supporting a traumatized cat’s recovery.
Remember, by being vigilant and responsive, we can make a positive difference in their lives.
